Maintenance Work Management
About this course
In this course you will gain the necessary work planning and scheduling knowledge and skills to:
- Increase the amount of maintenance work being accomplished without any additional resources.
- Free up labour resources and reallocate them to value-adding activities.
- Introduce continuous improvement activities to your current maintenance planning processes.
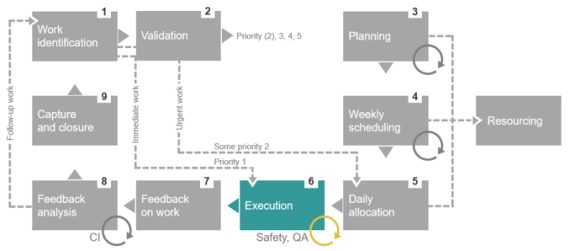
You will get to grips with the requirements of each of the steps in the Maintenance Work Management cycle, associated responsibilities and best practices. The efficient processing of tactical and non-tactical work through the cycle will ensure that you drive asset reliability improvements while efficiently using available resources.
Sound Planning and Scheduling principles, when applied at your plant will ensure that you have a standardised, repeatable process.
Outcomes
Evaluate and compare different Maintenance Work Management cycles
Explain how software applications and document controls can meet the requirements of Maintenance Work Management
Identify and prioritise work arising through notifications or work requests
Describe the benefits and explain the different roles and responsibilities when following a controlled Maintenance Work Management process
Scope and plan the work arising based on the notification or work requests
Apply effective planning techniques for tactical and non-tactical maintenance
Monitor execution activities and review work order feedback for optimisation purposes
Interpret production plans, resource requirements and opportunities for tactical maintenance
Discuss and implement solutions for recurring repair and maintenance problems and the optimisation of basic maintenance strategies
Analyse and interpret Maintenance Work Management reports for management and control purposes
Introduction
This module provides you with an introduction to the maintenance management model that supports a healthy maintenance work management process. The module provides the benefits and details the justification for the investment in a robust maintenance work management process.
Process Overview
This module builds on the maintenance management model from the introduction and provides the context within the asset life cycle. You will be introduced to the documentation and various information and software systems that are integrated with maintenance work management.
Validation and Approval Process
This is the first module that starts to unpack the Maintenance Work Management cycle; it emphasises the need for quality data from the source and demonstrates how effective validation drives an efficient process to the end.
Planning and Scheduling Principles
This modules unpacks the 12 principles of planning and scheduling that underpin all the decisions and activities that planners and schedulers should be making.
Execution and Feedback Process
This module emphasises the transfer of responsibility from the planning department to the first line supervisors responsible for how the work will be executed. It also looks at how the process loop is closed, ensuring a robust continuous improvement cycle for maintenance work management.
Planning Activities
In this module we apply the six planning principles and dig deep into the planner’s responsibilities and activities necessary to structure a comprehensive work package for execution.
Scheduling Activities
In this module we apply the six scheduling principles and provide the scheduler with the tools to utilise the information in the EAM system to be able to rank the work from the backlog, ensuring that the most important work is executed in an environment where resources are limited.
Resourcing
The interaction between resourcing, planning, scheduling and work execution requires mutual understanding and coordinated prioritisation, this module looks at the different aspects of this.
Long Term Work Plan
The long term workplan and the alignment of the operating environment constraints with the maintenance and reliability expectations is critical. This module explores how the long term workplan can be used to optimise the use of maintenance and external resources.
Tactics Optimisation
Having explored optimisation opportunities arising from the Long Term Work plan you are introduced to some fundamental principles of maintenance tactic development and this modules will open your eyes to a broader set of opportunities for further optimisation.
KPIs, Reporting and Analysis
Then last, but by no means least, we wrap-up the course by exposing you to typical work management KPIs are used in industry and how these can be used to optimse planning, scheduling and work management.
Who should attend?
- Maintenance supervisors
- Maintenance planners
- Maintenance schedulers
- Maintenance coordinators
- Maintenance foremen
Format and duration
- 3 day face to face classroom
- 6 x 4 hours Virtual classroom
- Blended learning with 8 hours virtual classroom activity and 16 hours of self-directed elearning
Terms and conditions of registration and use
All registrations received are regarded as confirmed and subject to the following:
- Payment must be made before the course start date or within 30 days of invoice date, whichever occurs first. Once payment has been made, please send proof thereof via email to: pragma.academy@pragmaworld.net.
- Refunds and/or substitutions are not applicable if a learner has: enrolled for a course and accessed it via the Pragma Academy Learning Management System; or attended a classroom session; or has enrolled, but failed to attend without notifying the Pragma Academy at least seven (7) working days prior to course start date.
- Refunds and/or substitutions are applicable: if cancellation is received in writing at least fifteen (15) working days before the scheduled start date of the course, a full refund is applicable; if cancellation is received in writing at least seven (7) working days before the scheduled start date of the course, a 50% refund is applicable; if a learner who enrolled in a course due to take place in less than fifteen (15) working days, sends a substitution learner subject to the substitution learner meeting the minimum prerequisite qualification requirements.
- It is the learner's responsibility to ensure that they meet the prerequisite requirements for a course they are enrolling in. Proof of suitable prerequisite qualifications will be required.
- Pragma reserves the right to cancel any advertised course due to insufficient enrolments or conditions beyond our control.